Total Knee Replacement Surgery
What is Knee Replacement Surgery?
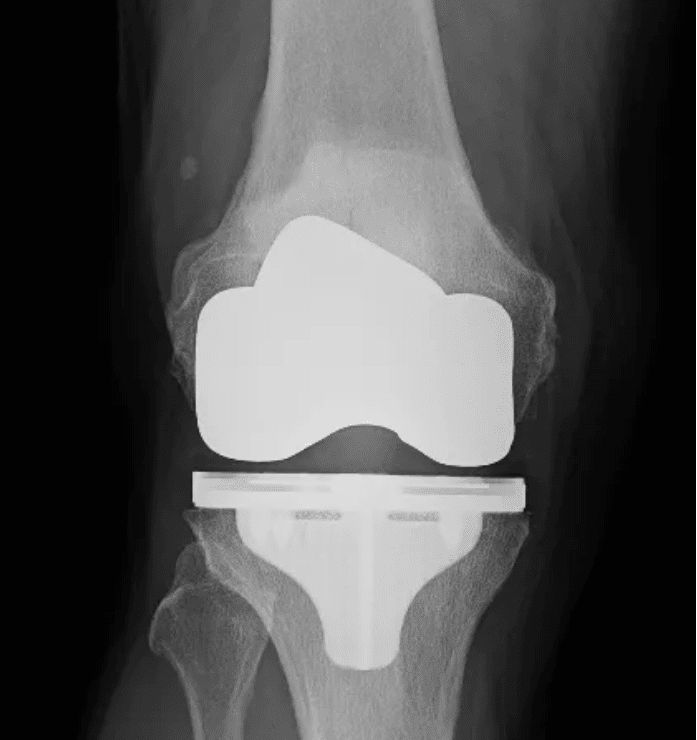
Knee Replacement Surgery, also known as knee arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure to relieve pain and improve the function of a damaged or arthritic knee joint. It involves replacing the damaged joint surface with a prothesis. It also involves restoring leg alignment and range of movement and stability. The prothesis is made of a surgical alloy - Cobalt-chromium-molybdenum (Co-Cr-Mo), a metal alloy used in many engineering and medical applications. It's known for its strength, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance. The plastic insert that is between the tibial and femoral components is made of highly cross-linked polyethylene (HXLPE) - a synthetic plastic which serves to replace the cartilage and meniscus in the joint. Your new knee replacement can be expected to last for decades (96% are still functioning after 10 years).
Knee replacement surgery is recommended for patients with severe knee pain, limited mobility, and reduced quality of life due to conditions that affect the knee joint.
How do we improve outcomes following Total knee replacement
Minimise infection - Peri-operative anti-biotics, multiple pre-surgical antiseptic washes, intra-articular antibiotics
Minimise trauma - Avoid use of tourniquet around thigh, careful soft tissue protection, and Sub-vastus muscle sparing approach.
Minimise error - Use Robotic technology to make the saw cuts accurate. Tibia first technique to maximise intra-operative checks.
Who is Suitable for Knee Replacement Surgery?
The procedure is usually recommended for patients who suffer from pain and loss of function from arthritis or other knee degeneration and have failed to achieve satisfactory results from other conservative methods of therapy over time.
Each patient is assessed individually, but candidates will commonly;
- Suffer Pain
- Restricted Mobility that interferes with daily life
- Stiffness, Deformity or Swelling.
- Consistent with medical imaging
These symptoms usually have been present for many months or years, often worsening over time. The decision to undergo knee replacement surgery is individualised and should be made in consultation with a healthcare professional.
Benefits of Total Knee Replacement Surgery
The benefits following surgery are the relief of arthritis symptoms. These include
Pain Relief
- One of the primary reasons for undergoing TKR is to eliminate or significantly reduce chronic knee pain caused by arthritis or joint damage.
- Remove the arthritic 'catching' and 'locking'.
Enhanced Quality of Life
- Patients can return to an active lifestyle, participate in hobbies, and experience improved mental well-being due to reduced pain and increased independence.
Correction of Deformities
- Knee replacement can correct alignment issues, such as bow-legged or knock-kneed conditions, improving overall posture and gait.
Long-Lasting Results
- Modern knee implants are durable, with many lasting 15–30 years or longer, reducing the need for revision surgery.
Total Knee Replacement Procedure
The procedure is designed to be performed with minimal local trauma
- The knee joint is exposed using a minimally invasive approach
- The damaged portions of the femur and tibia are then cut at the appropriate angles using a high-tech intra-operative computerised navigation system
- Trial components are then inserted to check the accuracy of these cuts and determine the plastic thickness required to place between these two components.
- The patella (kneecap) will need to be resurfaced in nearly all cases.
- The real components are inserted without cement but 'pressfit', and the knee is again checked for implant fit, alignment and stability.
- The knee is then carefully closed with dissolving sutures and skin glue. Sterile waterproof dressings and a compression bandage are applied.
Why is Rehabilitation for TKR Essential?
Rehabilitation has many different forms
- Independent home and gym exercise program
- Outpatient physiotherapy
- 'In the home' rehab - the physio may visit you at home
- Inpatient rehabilitation.
No one type of therapy is necessarily better. The aim of therapy is to promote independence.
Preparation Before Knee Replacement
- Schedule a consultation with an orthopaedic surgeon who specialises in knee replacements. Discuss your symptoms, medical history, and expectations.
- Undergo a thorough medical evaluation to assess your overall health and suitability for surgery. This may include blood tests, imaging scans, and other diagnostic tests.
- Follow your surgeon's recommendations for pre-operative preparation, which may include stopping certain medications, adhering to dietary guidelines, and arranging for post-operative support at home.
- In some cases, pre-operative physical therapy may be recommended to strengthen the knee muscles and improve joint function before surgery.
Post-Op Care After an Approach Knee Replacement
Recovery and rehabilitation are essential aspects of the postoperative phase:
- Hospital stay: Most patients spend a brief period after surgery, typically 1-3 days, to monitor their progress.
- Physical therapy: Physical therapy plays a crucial role in recovery. A customised rehabilitation plan will be created to help you regain strength, flexibility, and mobility.
- Pain management: Your healthcare team will manage pain through medication and other pain relief techniques. Medication include paracetamol and opioids such as Palexia and Endone. Its important to try and cease opioid medications by week 3 to avoid dependence.
- Activity progression: Gradually, you will be encouraged to increase your activity level, starting with walking and advancing to more complex movements.
- Follow-up appointments: Attend all follow-up appointments with your surgeon to monitor your progress and address concerns.
- Return to normal activities: The timeline for returning to normal activities varies but may take several weeks to months.
Knee Replacement Surgery Risks
While knee replacement surgery is generally safe, there are potential risks and complications to be aware of:
- Infection: Any surgical procedure carries a risk of infection. Surgical sites can become infected, requiring treatment with antibiotics or, in severe cases, additional surgery.
- Blood Clots: Blood clots can form in the leg's deep veins (deep vein thrombosis) or travel to the lungs (pulmonary embolism). Preventative measures such as blood-thinning medications and compression stockings are used to reduce this risk.
- Nerve or Blood Vessel Damage: There is a small risk of nerve or blood vessel damage around the knee joint during surgery, which could lead to numbness, weakness, or other complications.
- Implant Problems: In rare cases, issues with the knee prosthesis, such as loosening, dislocation, or wear, may require additional surgeries.
- Stiffness or Limited Range of Motion: Some patients may experience stiffness or limited range of motion in the knee, which may require ongoing physical therapy.
- Allergic Reaction: Allergic reactions to materials used in the prosthesis are extremely rare but possible.
- Pain: While knee replacement surgery is intended to relieve pain, some patients may experience persistent or new pain after surgery, requiring further evaluation and management.
Post-surgery symptoms
Initially the patients experience common things like;
- Pain
- Swelling
- Bruising
- Numbness adjacent to the wound
Patients may also experience
- Loss of appetite, constipation, altered sleep pattern and reduced mood and feeling socially withdrawn.
The lasting prognosis for knee replacement surgery is generally very positive.
- Pain Relief: Most patients experience significant pain relief after surgery, which improves their overall quality of life.
- Improved Mobility: Knee replacement surgery can restore mobility and joint function, allowing patients to engage in previously impossible activities.
- Longevity: The artificial joint components are designed to be durable, and many patients enjoy long-lasting results that can last for decades.
- Enhanced Quality of Life: Knee replacement surgery often improves quality of life, as patients can return to daily activities and hobbies with less pain and better mobility.
Individual outcomes can vary based on factors such as the patient's overall health, adherence to post-operative care, and the extent of joint damage. These positive changes take time, commonly 3-9 months. Patients will commonly continue to improve for 18 months post surgery.